Meniscus Repair
Meniscus repair represents the gold standard treatment for suitable tears, offering the best long-term outcomes for joint health and function.
What Is Meniscus Repair?
Meniscus repair with arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to restore torn meniscal tissue in the knee joint. The meniscus consists of two C-shaped pieces of fibrocartilage – the medial meniscus (inner) and lateral meniscus (outer) – that act as shock absorbers and stabilizers between the thighbone and shinbone.
Unlike meniscal removal (meniscectomy), meniscus repair focuses on preserving and healing the natural tissue by suturing the torn edges back together. This approach maintains the meniscus’s crucial functions of load distribution, joint stability, and cartilage protection.
Types of Meniscal Tears
Repairable Tears
- Longitudinal tears: Run parallel to the meniscus fibers and have excellent healing potential
- Bucket-handle tears: Large longitudinal tears that can flip over, causing mechanical locking
- Peripheral tears: Located in the vascular “red zone” with good blood supply for healing
- Acute traumatic tears: Fresh tears in younger patients with healthy meniscal tissue
Non-Repairable Tears
- Degenerative tears: Complex, frayed tears in older patients with poor tissue quality
- Radial tears: Cut across meniscal fibers, disrupting the hoop stress mechanism
- Central avascular tears: Located in the “white zone” with poor blood supply
- Extensively damaged tissue: Multiple tear patterns with insufficient healthy tissue
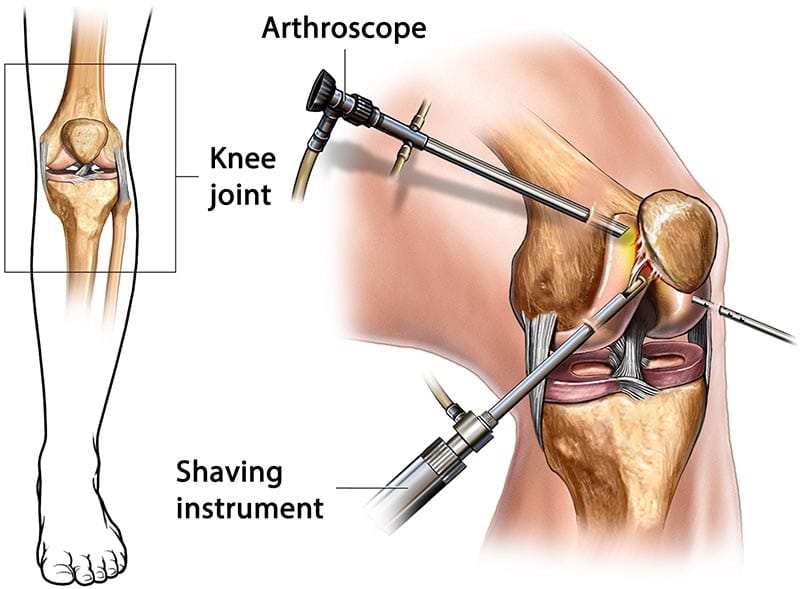
What Happens During Meniscus Repair?
The arthroscopic meniscus repair is performed as outpatient surgery, typically taking 45-90 minutes:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is positioned supine with the knee flexed and accessible for arthroscopic portals
- Arthroscopic Evaluation: The surgeon examines the entire meniscus to assess tear pattern, tissue quality, and repairability
- Tear Preparation: The torn edges are cleaned and prepared to promote healing, removing any frayed or unstable tissue
- Repair Technique Selection: Based on tear location and pattern, the surgeon chooses from various repair methods
- Suture Placement: Specialized instruments place sutures to bring torn edges together with appropriate tension
- Repair Verification: The repair is tested through range of motion to ensure stability and proper healing alignment
Advantages of Meniscus Repair
1. Joint Preservation
- Maintains shock absorption function, reducing cartilage stress
- Preserves joint stability and proprioception
- Prevents accelerated arthritis that often follows meniscectomy
- Maintains normal knee biomechanics and load distribution
2. Long-Term Joint Health
- Significantly reduces arthritis risk compared to meniscal removal
- Preserves cartilage integrity over decades
- Maintains joint space and prevents bone-on-bone contact
- Supports active lifestyle throughout life
3. Superior Functional Outcomes
- Better long-term knee function compared to meniscectomy
- Improved sports performance and return to activities
- Enhanced knee stability during dynamic movements
- Reduced pain and swelling in the long term
4. Younger Patient Benefits
- Prevents early arthritis in active individuals
- Supports continued sports participation at competitive levels
- Maintains knee health for decades of active use
- Avoids future joint replacement procedures
Making the Right Choice
Meniscus repair with arthroscopy represents a joint preservation strategy that prioritizes long-term knee health over short-term convenience. While recovery takes longer than simple meniscal removal, the long-term benefits for joint health, function, and quality of life make repair the preferred option for suitable candidates.
The key is proper patient selection, experienced surgical technique, and commitment to the rehabilitation process to achieve optimal outcomes and lifelong knee health.
